Cranial Nerves
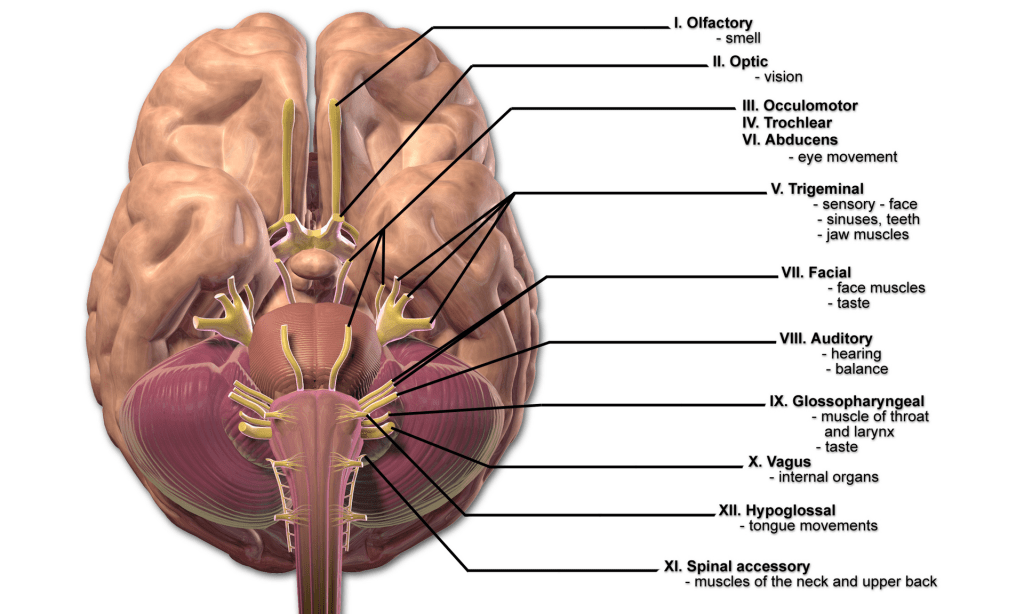
There are 12 cranial nerves, enumerated by Roman numerals. They are specialized PNS nerve bundles originating from the brain (or cranium), and are visible on the brain’s ventral surface
Functional classification
- Sensory: I (Olfactory), II (Optic), VIII (Vestibulocochlear)
- Motor: III (Oculomotor), IV (Trochlear), VI (Abducens), XI (Accessory), XII (Hypoglossal)
- Mixed (both sensory/motor functions): V (Trigeminal), VII (Facial), IX (Glossopharyngeal), X (Vagus)
- Special sensory: I (Smell), II (Vision), VIII (Equilibrium/Hearing), VII/IX/X (Taste)
Embryological classification
- Branchial (pharyngeal arch) nerves: V, VII, IX, X
- Somite-derived (eye/tongue muscles): III, IV, VI, XII
Skull foramina classification: anatomical exit sites
- Specifics in Table 1
Cranial nerve comparison
Special examples
- Taste: VII, IX, X
- Blinking: V1 (afferent), VII (efferent)
- Reflexes
- Vestibulo-ocular (VOR): VIII (afferent), III, IV, VI (efferent)
- Acoustic (stapedius muscle): VIII (afferent), VII (efferent)
- Pupillary light: II (afferent), III (efferent)
- Corneal: V1 (afferent), VII (efferent)
- Gag: IX (afferent), X (efferent)
| CN | Origin | Foramina | Destination | Functional classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (Olfactory)1 | Olfactory epithelium | Cribriform plate of ethmoid | Olfactory bulbs | Sensory (special sense) |
| II (Optic) | Retina | Optic canals of sphenoid | Optic chiasm (converging point) | Sensory (special sense) |
| III (Oculomotor) | Midbrain (oculomotor nucleus) | Superior orbital fissures of sphenoid | Extrinsic eye muscles (4/6), levator palpebrae superioris, pupillary constrictor | Motor |
| IV (Trochlear) | Midbrain (trochlear nucleus) | Superior orbital fissures of sphenoid | Superior obliques | Motor |
| V (Trigeminal) | Cornea, forehead, upper eyelid (V1), midface, teeth, nasal cavity (V2), lower face/teeth (V3) | Superior orbital fissures (V1/ophthalmic branch), foramen rotundum (V2/maxillary), foramen ovale (V3/mandibular) | Pons sensory nuclei (V1-3), mastication muscles (V3) | Mixed (face) |
| VI (Abducens) | Pons | Superior orbital fissures of sphenoid | Lateral rectus muscle | Motor |
| VII (Facial) | Anterior 2/3 of tongue (sensory), motor nuclei of pons (motor) | Internal acoustic meatus | Nucleus solitarius (sensory), facial expression muscles, salivary/lacrimal glands (motor) | Mixed (face) |
| VIII (Vestibulocochlear) | Vestibular apparatus (vestibular branch), cochlear/Organ of Corti (cochlear branch) | Internal acoustic meatus of temporal | Vestibular/cochlear nuclei of pons and medulla oblongata | Sensory (special sense) |
| IX (Glossopharyngeal) | Posterior 1/3 tongue, pharynx/palate, carotids(sensory), nucleus ambiguus of medulla oblongata (motor) | Jugular foramina between occipital/temporal | Nucleus solitarius (sensory), stylopharyngeus muscle, parotid gland (motor) | Mixed (head, neck): sensory (superior/jugular and inferior/petrosal ganglia) |
| X (Vagus) | Pharynx, epiglottis taste, external ear apparatus, diaphragm, visceral thoracic-abdominopelvic organs (sensory), motor nuclei in MO (motor) | Jugular foramina between occipital/temporal | Sensory nuclei, autonomic centers of MO (sensory), larynx/pharynx muscles (motor) | Mixed (thorax, abdomen): sensory (superior/jugular and inferior/nodose ganglia) |
| XI (Accessory) | Motor nuclei of SC and MO | Jugular foramina between occipital/temporal | Voluntary muscles of palate/pharynx/larynx (internal branch, joining vagus), sternocleidomastoid/trapezius (external branch) | Motor |
| XII (Hypoglossal) | Motor nuclei of MO | Hypoglossal canals of occipital | Extrinsic/intrinsic tongue muscles | Motor |
Functional tests (physical exam)
I: smell
II: visual acuity (Snellen’s), pupillary reflex
III: EOMs/H Test (finger in H pattern to test for normal movement of extra-ocular muscles), accommodation reflex, eyelid droop
IV: eyes look down/in
V: test light touch/pain, jaw clench, corneal reflex (afferent; doesn’t feel stimulus, no consensual blinking)
VI: eyes look side/laterally, Parks-Bielschowsky-Helveston head tilt Test
VII: facial symmetry, taste test, corneal reflex (efferent; feels stimulus, no consensual blinking)
VIII: finger rub, Rinne/Weber, Romberg Test (stand feet together eyes closed and open, observe for significant loss of balance)
IX: gag reflex (afferent), swallowing reflex
X: swallowing reflex
XI: turning head, shrug shoulder
XII: sticking out tongue


Leave a comment