Atherosclerosis
General Information
What is it?
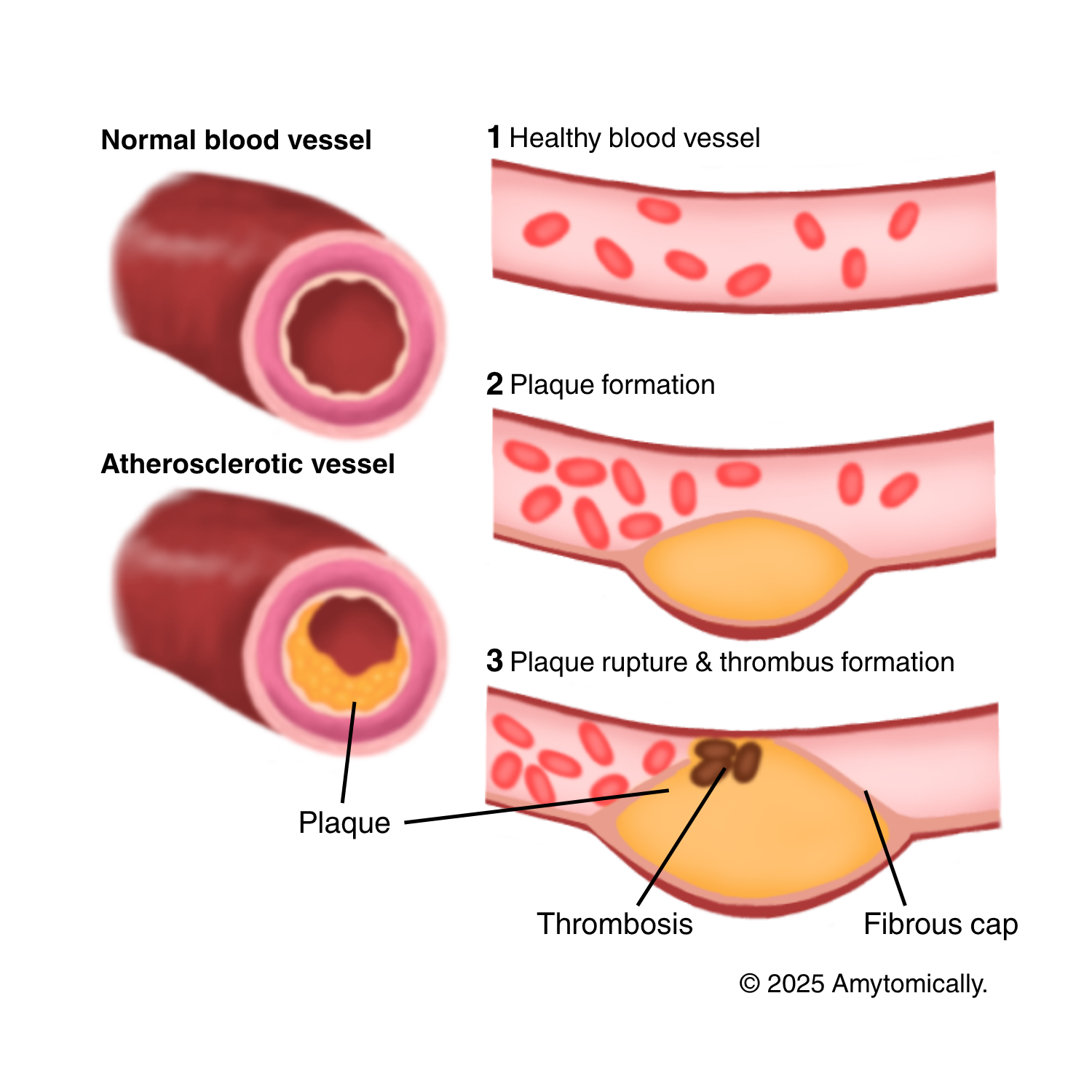
Inflammation derived from lipid deposits (principally low-density lipoproteins/LDLs) in tunica media of blood vessels, which lead to plaque formation
Extremely high incidence within older individuals, and is considered the major cause of other cardiovascular diseases/CVD (which is the leading cause of death)
Risk Factors: hypercholesterolemia, older age, male, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, hypertension (HT), genetic predisposition, diabetes mellitus/Type 1
Signs and symptoms across the body:
- In heart: causes chest pain/angina
- In brain: weakness in limbs, drooping muscles, transient ischemic attack/TIA
- In extremities: peripheral artery disease/PAD
- In kidneys: increased blood pressure/BP, renal failure
Arteriosclerosis vs Atherosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis: hardening and/or calcification of arteries
Atherosclerosis: subtype of arteriosclerosis, where the closing of arteries is due to fatty plaque formation
Evaluation: catheterization, angiogram, CT
Pathophysiology:
- Fatty streak deposition in tunica intima
- LDLs are trapped by proteoglycans and modified, disrupting the endothelial barrier
- Fibrous cap formation (migration of smooth muscle cells) mediated by IGF, angiotensin II as plaque continues to grow
- Plaque rupture occurs when fibrous cap weakens
- The thrombus (blood clot) can be released and lead to complications depending on location of the artery
Treatment
Protective treatment/lifestyle changes: increased aerobic exercise, diet of low red meats and trans fats, diminish smoking frequency
To control BP: ACE inhibitors, Angiotensin II blockers (ARBs)
To lower cholesterol levels: statins
Aspirin for pain
Surgical procedures (revascularization)
- Balloon coronary angioplasty or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI):
- Insert catheter (thin tube) into accessible vessel up to the coronary artery → balloon is inflated to increase blood flow and push plaque away → can insert stent to keep the artery open after balloon is removed
- Coronary artery bypass: graft a healthy vein to the area of the blockage, bypassing the plaque/occluded area
Complications
In heart
- Ischemic heart disease or coronary artery disease/CAD
- Arrythmias
In extremities:
- Peripheral artery disease/PAD
- Deep vein thrombosis in lower extremities
Others: muscle pain or other paresthesias, stroke


Leave a comment