Mechanoreceptors
Things to know…
What are they? Somatosensory cells that respond to various physical stimuli or sensations
Neural crest cell origination (debated): TFs MafA and c-Maf help induce differentiation
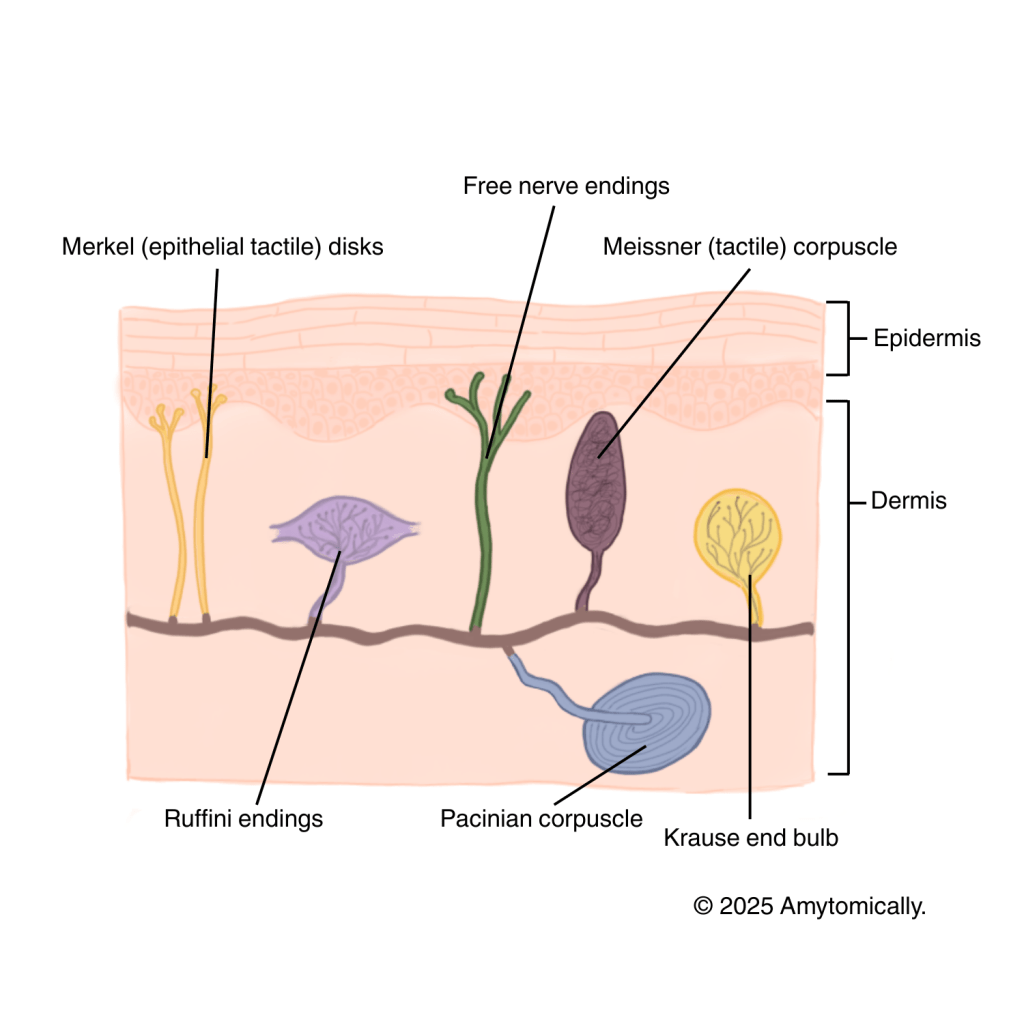
| Mechanoreceptor | Encapsulation1 | Receptive field and frequency2 | Depth in integument | Location | Type of touch | Fibers | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free nerve endings | No | Typically SA | Throughout epidermis and dermis, especially in deeper epidermis and papillary dermal layers | Widespread throughout body | Nociception, temperature, coarse touch, itching | C fibers (unmyelinated if for pain/warmth) or Alpha-delta fibers (sharp pain/cold) | Thin axons and highly branched, little structural differentiation |
| Krause end bulbs | Yes | Low-threshold SA | Deep dermis or subcutaneous tissue | Penile and clitoris skin | Low frequency vibrations, light touch, cold | Alpha-beta | Ovoid; thin collagenous capsules |
| Merkel/tactile discs | No | SA1 | Basal epidermis | Fingertips, lips (high sensitivity areas), hands | Light touch | Alpha-beta (single, myelinated afferent) | Expanded nerve endings, joined to keratinocytes via desmosomes |
| Meissner/tactile corpuscles | Yes | RA1 | Dermal papillae | Especially prominent on hairless areas of fingertips, palms, soles, and also eyelids, external genitalia | Low frequency vibrations, light touch | Alpha-beta | Elliptical axons with schwann cells; numbers decline after puberty; two point discrimination test |
| Ruffini endings | Yes | SA2 | Dermis | All skin, joint capsules, ligaments/tendons | Skin stretch/torque, prolonged pressure, joint movement | Alpha-beta | Collagenous fusiform capsules anchored to CT; dendrites intertwined with collagen network |
| Pacinian/lamellated corpuscles | Yes | RA2 | Deep dermis or subcutaneous tissue | Fingers, joints, interosseous membranes (detect skeletal muscle vibration), mammary glands, genitalia, organ CT (e.g., rectal wall, urinary bladder) | Deep pressure, high frequency vibrations, coarse and sustained touch | Alpha-beta | Large and ovoid; has thin concentric lamellae and highly branched unmyelinated axon with single dendrite |
Updated: 7/26/25


Leave a comment